Advancing Global Clinical Standards with Senzime
June 17, 2024
By Britta Weber, Clinical Director EMEA and APAC

In this blog series, we celebrate Senzime's 25-year anniversary by reflecting on our past, present, and future.
Our Clinical Director for EMEA and APAC shares her insights on how the TetraGraph quantitative monitoring system helps to enhance healthcare standards and patient care around the world.
Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs) are highly potent, essential for facilitating intubation, and invaluable to surgeons. However, their effects must be properly reversed during extubation to prevent postoperative complications. These complications, following the administration of muscle relaxants, have been well-documented for many years. Clinical assessment and subjective monitoring with peripheral nerve stimulators are not sufficient to prevent residual neuromuscular block (rNMB)(1).
The large-scale European multicenter POPULAR study highlights that postoperative pulmonary complications occur both with and without reversal drugs(2). Additionally, the study reveals that only 25% of the 4,182 patients received quantitative neuromuscular monitoring(3). Among these monitored patients, 1,343 were extubated with a TOF ratio of less than 0.9(4). Furthermore, only 68% of patients in this monitored group were extubated at a TOF ratio of 0.9 or higher, meaning that at least 32% were still at potential risk of postoperative complications despite undergoing quantitative neuromuscular monitoring.
Moreover, 76% of the 17,150 patients receiving NMBAs did not receive any quantitative neuromuscular monitoring, thereby facing a potential risk for postoperative complications due to NMBAs. Further analysis of the POPULAR study data indicates that postoperative complications can only be significantly reduced with a TOF ratio of 0.95 or higher. Consequently, the number of inadequately monitored patients is even higher than initially thought.
The quantitative monitors used in this study are all based on acceleromyography (AMG) technology, which measures movement and acceleration. However, AMG technology has known disadvantages, such as the “reverse fade” phenomenon during calibration, which can lead to an overestimation of recovery. Due to these limitations, the current ASA and ESAIC guidelines recommend extubating at a TOF ratio of 95% or higher (5,6,7,8,9).
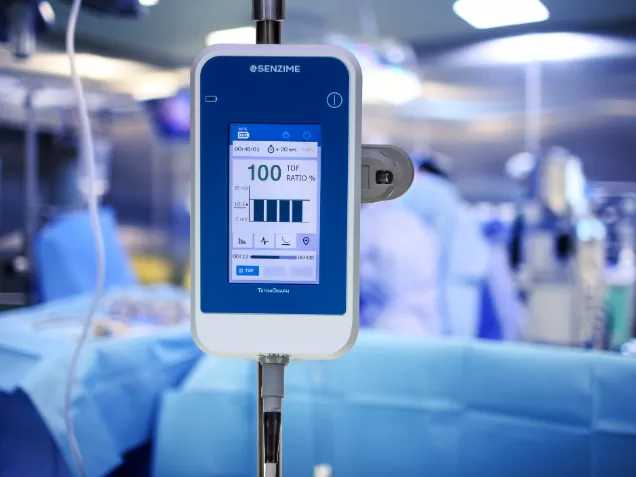
Senzime's new technology in the TetraGraph system addresses existing issues with current monitoring methods. Utilizing electromyography (EMG), it measures action potentials, rendering movement irrelevant. This allows the TetraGraph neuromuscular monitor to be used even when the patient's arms are tucked. Thanks to the high accuracy of EMG, overestimation of recovery is eliminated, and normalization of measured values relative to the baseline TOF ratio is unnecessary (10).
These advantages make the TetraGraph system easy to use and quick to set up for patients. This represents the new standard in scientific and technological advancements.
As more procedures are performed laparoscopically and robotically, patients' arms are often tucked to their bodies, presenting additional challenges for care providers (11). Deep relaxation is typically required during these procedures, and both deep relaxation and full recovery must be ensured before extubation.
Learn more about TetraGraph and request a complementary demo at the TetraGraph product page.
References
- Saager L, Maiese EM, Bash LD, Meyer TA, Minkowitz H, Groudine S, Philip BK, Tanaka P, Gan TJ, Rodriguez-Blanco Y, Soto R, Heisel O. Incidence, risk factors, and consequences of residual neuromuscular block in the United States: The prospective, observational, multicenter RECITE-US study. J Clin Anesth. 2019 Aug;55:33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2018.12.042. Epub 2018 Dec 27. PMID: 30594097.
- Kirmeier E, Erikkson LI, Lewald H, et al. Post-anaesthesia pulmonary complications after use of muscle relaxants: a prospective multicentre observational study (POPULAR). Lancet Respir Med 2019; 7: 129–40.
- de Boer HD, Brull SJ, Naguib M, Murphy GS, Kopman AF. Neuromuscular monitoring and reversal: responses to the POPULAR study. Lancet Respir Med. 2019 Feb;7(2):e4. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30527-7. PMID: 30709453.
- Blobner M, Hunter JM, Ulm K, Hollmann M. Neuromuscular monitoring and reversal: responses to the POPULAR study - Authors' reply. Lancet Respir Med. 2019 Feb;7(2):e7-e8. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30462-4. PMID: 30709456.
- Suzuki T, Fukano N, Kitajima O, Saeki S, Ogawa S. Normalization of acceleromyographic train-of-four ratio by baseline value for detecting residual neuromuscular block. Br J Anaesth. 2006 Jan;96(1):44-7. doi: 10.1093/bja/aei273. Epub 2005 Nov 18. PMID: 16299046.
- Kopman AF. Normalization of the acceleromyographic train-of-four fade ratio. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005 Nov;49(10):1575-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2005.00880.x. PMID: 16223413.
- Liang, Sophie S. BSc (Adv.)*; Stewart, Paul A. MBBS, FANZCA†; Phillips, Stephanie BMed, FANZCA, FRCA†. An Ipsilateral Comparison of Acceleromyography and Electromyography During Recovery from Nondepolarizing Neuromuscular Block Under General Anesthesia in Humans. Anesthesia & Analgesia 117(2):p 373-379, August 2013. | DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182937fc4
- Fuchs-Buder T, Romero CS, Lewald H, Lamperti M, Afshari A, Hristovska AM, Schmartz D, Hinkelbein J, Longrois D, Popp M, de Boer HD, Sorbello M, Jankovic R, Kranke P. Peri-operative management of neuromuscular blockade: A guideline from the European Society of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2023 Feb 1;40(2):82-94. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000001769. Epub 2022 Nov 15. PMID: 36377554.
- Thilen SR, Weigel WA, Todd MM, Dutton RP, Lien CA, Grant SA, Szokol JW, Eriksson LI, Yaster M, Grant MD, Agarkar M, Marbella AM, Blanck JF, Domino KB. 2023 American Society of Anesthesiologists Practice Guidelines for Monitoring and Antagonism of Neuromuscular Blockade: A Report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Neuromuscular Blockade. Anesthesiology. 2023 Jan 1;138(1):13-41. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000004379. PMID: 36520073.
- Zain Wedemeyer, Kelly E Michaelsen, Srdjan Jelacic, Willis Silliman, Aidan Lopez, Kei Togashi, Andrew Bowdle; Accuracy and Precision of Three Acceleromyographs, Three Electromyographs and a Mechanomyograph Measuring the Train-of-Four Ratio in the Absence of Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs. Anesthesiology Newly Published on May 10, 2024. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000005051
- Chiumello D, Coppola S, Fratti I, Leone M, Pastene B. Ventilation strategy during urological and gynaecological robotic-assisted surgery: a narrative review. Br J Anaesth. 2023 Oct;131(4):764-774. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2023.06.066. Epub 2023 Aug 3. PMID: 37541952.
Britta Weber, Clinical Director EMEA & APAC at Senzime
If you have any further questions or require additional information, feel free to contact me and my colleagues.

Feel free to get in touch to talk to a sales representative about latest technology advancements or request a complimentary demo.
