Enhancing patient safety with TetraGraph
A brief look into the ASA practice guidelines for neuromuscular blockade
Feb 29, 2024
By Michael Grey, Market Development Manager at Senzime US

In today's constantly evolving healthcare landscape, patient safety remains paramount. An essential aspect of ensuring patient well-being during surgical procedures involves monitoring neuromuscular blockade. With advancements in technology, the TetraGraph quantitative neuromuscular monitor has emerged as the monitor of choice for thousands of clinicians in this field.
This blog post aims to shed light on the innovative features of the TetraGraph monitor and its alignment with the 2023 ASA practice guidelines for neuromuscular blockade management.
Neuromuscular blockade refers to a condition induced during certain surgeries or procedures that relaxes patient skeletal muscles to optimize surgical conditions and overall safety and efficacy. Monitoring the level of neuromuscular blockade is crucial in preventing inadequate or excessive muscle relaxation, which could otherwise lead to complications.
Traditionally in the US, subjective assessments have been used for monitoring neuromuscular blockade. These include relying on clinical signs such as patient head lift or hand grip. The peripheral nerve stimulator (PNS) device is another subjective assessment that relies on the provider to subjectively observe patient twitch response. However, these methods lack accuracy and reliability.
The more reliable way to accurately monitor neuromuscular blockade is to use an objective quantitative device.
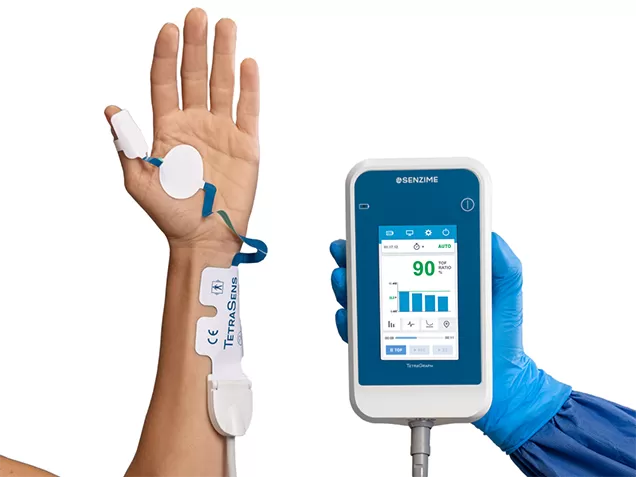
TetraGraph represents the next-generation quantitative neuromuscular monitoring. It is a cutting-edge device designed to enhance precision and reliability. By utilizing electromyography (EMG), this monitor provides accurate and real-time feedback on the patient's level of muscle relaxation.
Here are four reasons for why TetraGraph is the monitor of choice compared to older technologies:
1. Objective assessment: Unlike subjective assessments, TetraGraph offers quantified visualizations of the patient’s response by measuring the evoked compound muscle action potential (CMAP). Clinically validated against the reference technology mechanomyography (MMG), TetraGraph’s unique peak-to-trough measurement of the EMG response produces an accurate, quantified result. TetraGraph calculates that data then displays it both numerically and graphically on the monitor as the patient’s train of four ratio, train of four count, post tetanic count, or single twitch response.
2. User-friendly interface: TetraGraph's intuitive interface simplifies operation, enabling you as a clinician to seamlessly integrate it into the workflow. A simple one-button start can be all that is needed to successfully monitor a patient for an entire surgical case. Customizations are available to interval and other settings with minimal interaction required from the provider.
3. Real-time feedback: With instant visual feedback, TetraGraph allows you to closely monitor a patient's neuromuscular response, ensuring optimal muscle relaxation throughout surgery. This can be particularly useful during times of rapid change such as onset of neuromuscular blocking agents like rocuronium and cisatracurium. Recovery can also be a time of rapid change when using reversal agents such as neostigmine or sugammadex. Real-time feedback also adds tremendous value to help optimize the timing and dosage of both paralytic and reversal medication. Not all patients metabolize or respond equally to medications. TetraGraph gives you real-time visibility to your patient’s status just before you give the medication, and how they respond after administering the medication.
4. Enhanced patient safety: By precisely titrating neuromuscular blocking agents, TetraGraph helps reduce the risk of inadequate paralysis intraoperatively while avoiding unnecessarily deep paralysis that requires excessive use of reversal medication. TetraGraph helps to achieve the optimal timing and dosage of paralytic and reversal agent if needed. Per the ASA guidelines, if your patient is already at a 90% train of four ratio quantitatively monitored at the ulnar nerve, then no reversal agent is needed. With greater accuracy and visibility to your patient’s status, TetraGraph contributes to individualized care for each patient’s needs while reducing the risk of postoperative residual muscle weakness and associated complications.
The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) is a renowned authority in anesthesia practice, and their guidelines shape industry standards. The 2023 ASA practice guidelines for neuromuscular blockade management emphasize the significance of utilizing quantitative monitoring during procedures involving neuromuscular blocking agents.
“We recommend quantitative monitoring over qualitative assessment to avoid residual neuromuscular blockade.”
- Stefan R Thilen et al. 2023 American Society of Anesthesiologists Practice Guidelines for Monitoring and Antagonism of Neuromuscular Blockade: A Report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Neuromuscular Blockade.
Quantitative monitors, like TetraGraph, can help to optimize patient care and mitigate complications associated with inadequate or prolonged muscle relaxation. The ASA Guidelines reference numerous peer-reviewed publications supporting this important update for clinicians. Refer to the guidelines for more information and check back with us for more blog posts on these recommendations.
As healthcare providers strive to enhance patient safety, incorporating the TetraGraph quantitative neuromuscular monitor into clinical practice holds immense promise. By offering objective and real-time feedback, this innovative device aligns with the 2023 ASA guidelines, empowering you as an anesthesia provider to optimize the administration of neuromuscular blocking agents and reversals. Embracing such advancements ensures safer surgical procedures and improves patient outcomes in the ever-evolving healthcare landscape.
We hope this blog post provides valuable insights into the TetraGraph quantitative neuromuscular transmission monitor and its relevance to the 2023 ASA guidelines.
Stephan R. Thilen, Wade A. Weigel, Michael M. Todd, Richard P. Dutton, Cynthia A. Lien, Stuart A. Grant, Joseph W. Szokol, Lars I. Eriksson, Myron Yaster, Mark D. Grant, Madhulika Agarkar, Anne M. Marbella, Jaime F. Blanck, Karen B. Domino; 2023 American Society of Anesthesiologists Practice Guidelines for Monitoring and Antagonism of Neuromuscular Blockade: A Report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Neuromuscular Blockade. Anesthesiology 2023; 138:13–41 doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000004379
TetraGraph quantitative neuromuscular monitor, product page
The TetraGraph EMG Algorithm: A Technical White Paper, published december 2023.
Michael Grey
Market Development Manager for Senzime US
If you have any further questions or require additional information, feel free to contact me and my colleagues.

Feel free to get in touch to talk to a sales representative about latest technology advancements or request a complimentary demo.
